Related projects
Project One:National Key Research and Development Program of China: "Key Technologies and Software for deep Mining and intelligent analysis of scientific literature content (Grant No.2022YFF0711900)"
Project Website:https://sciaiminer.las.ac.cn/
Project Background
Scientific and technological literature contains human knowledge and reflects scientific research results, which is the basis of knowledge service and intelligence analysis of literature and information agencies. The project aims at the important problem that literature and intelligence agencies urgently need to improve intelligent technology methods and means, effectively dig out deep knowledge content hidden in massive scientific and technological literature and make full use of it, break through intelligent key technologies, and develop independent software for knowledge service and intelligence analysis.
Overall Goal
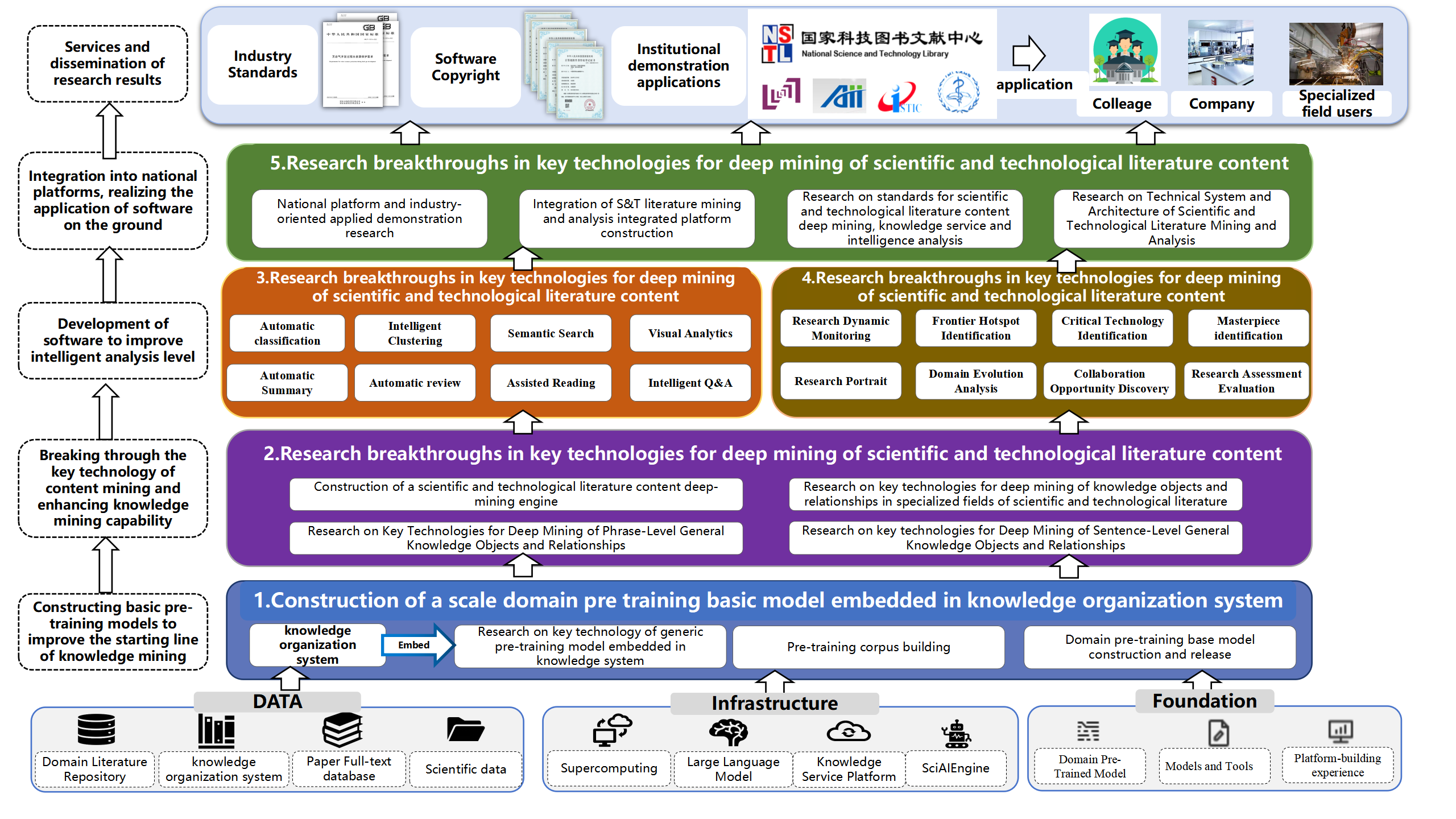
- Topic one: Construction of a scale domain pre training basic model embedded in knowledge organization system
- Topic two: Research breakthroughs in key technologies for deep mining of scientific and technological literature content
- Topic three: Research and development of intelligent knowledge service software system
- Topic four: Research and development of intelligent intelligence analysis software tools
- Topic five: Technology integration and sharing and application demonstration for national Science and technology document platform
Main Research Content
The research focus of the project is to break through the key technologies of deep mining and intelligent analysis of scientific and technological literature content, and develop autonomous software systems required to support scientific and technological literature knowledge services and intelligence analysis. The focus is on: Construction of a scale domain pre training basic model embedded in knowledge organization system; Key technologies for deep mining of scientific and technological literature content; Research and development of intelligent knowledge service software system; Research and development of intelligent intelligence analysis software tools; Technology integration and sharing and application demonstration for national Science and technology document platform.
Project Two:National Social Science Foundation of China: "Big data-driven research on semantic evaluation system of scientific and technological literature (Grant No.21&ZD329)"
Project Website:https://scisemeval.las.ac.cn/
Project Background
The current scientific and technological(S&T) evaluation system cannot penetrate into the content of literature, and cannot evaluate many fine-grained indicators of S&T literature, such as there is no effective means to evaluate the perfection of the research process, the value of the research, the rationality of the research methods, and the innovation of the results.
Overall Goal
- Topic one: Research on the theoretical basis of semantic evaluation of S&T literature driven by big data
- Topic two:Construction of a semantic evaluation method system for S&T literature driven by big data
- Topic three:esearch on key technologies for semantic evaluation of S&T literature driven by big data
- Topic four:Empirical analysis of semantic evaluation methods of S&T literature driven by big data
Main Research Content
The general idea of the project is to use S&T literature as a carrier to evaluate scientific research results or scientific research performance. Specifically, based on the semantic content and semantic environment of S&T literature, it researches and breaks through the technical methods of S&T evaluation based on semantic elements, and researches and constructs a new evaluation system that is "guided by the quality, contribution and performance of S&T innovation".
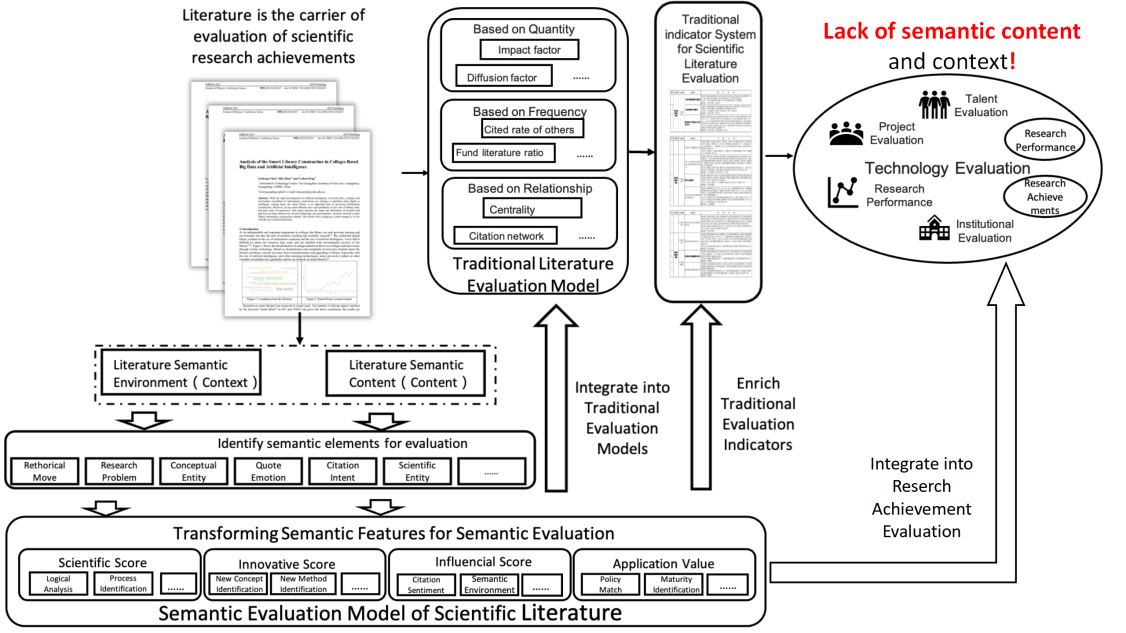
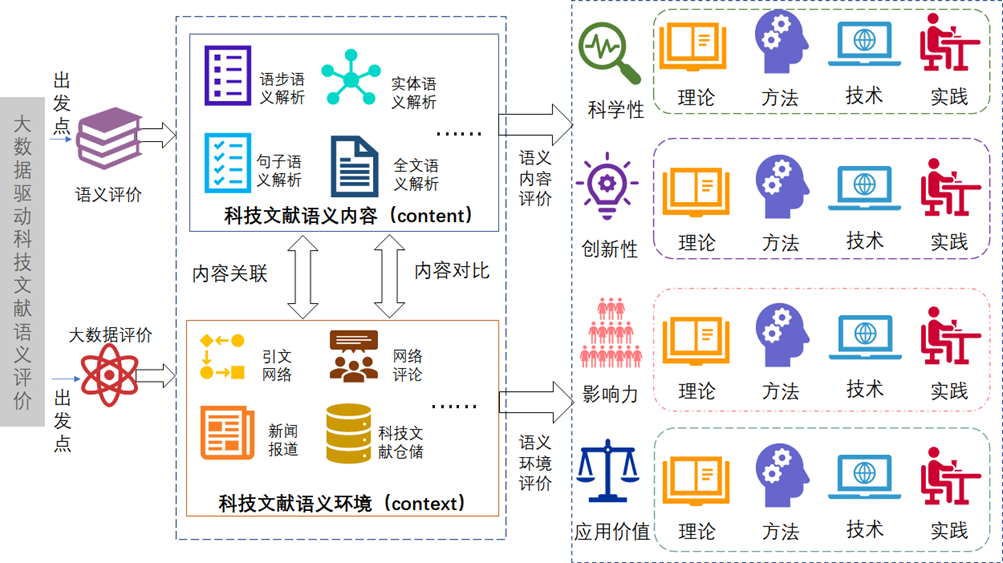
Taking the two key elements of big data and semantics as the starting point, the project analyzes the content of S&T literature from the semantic content and the external semantic environment. Through comparison and contrast, this project explores the characteristics of S&T literature in four dimensions: scientificity, innovation, influence and application value, and forms a semantic evaluation system of S&T literature driven by big data through the research of theory, method, technology and practice.
Project Three:Special Program for Building Information Literacy Capacity of the Chinese Academy of Sciences: "Construction of an Artificial Intelligence (AI) Engine Based on Scientific and Technological Literature Knowledge"
Project Background
The common sense (or knowledge) hidden in various types of literature is an essential foundation for AI technology and is the essence of its rapid breakthroughs. Digital libraries contain a wealth of scientific and technological literature resources, which are the most important carriers of human knowledge. These resources contain rich knowledge content, such as definitions, concepts, research background, research problems, research foundations, research approaches, theoretical tools and methods used in papers, scientific experiments conducted in papers, obtained experimental results, and formed research conclusions. It is an important task for digital library researchers and builders to reveal the knowledge in scientific and technological literature.
Overall Goal
- Construct and release a Chinese scientific paper pre-training basic language model (CsciBERT)
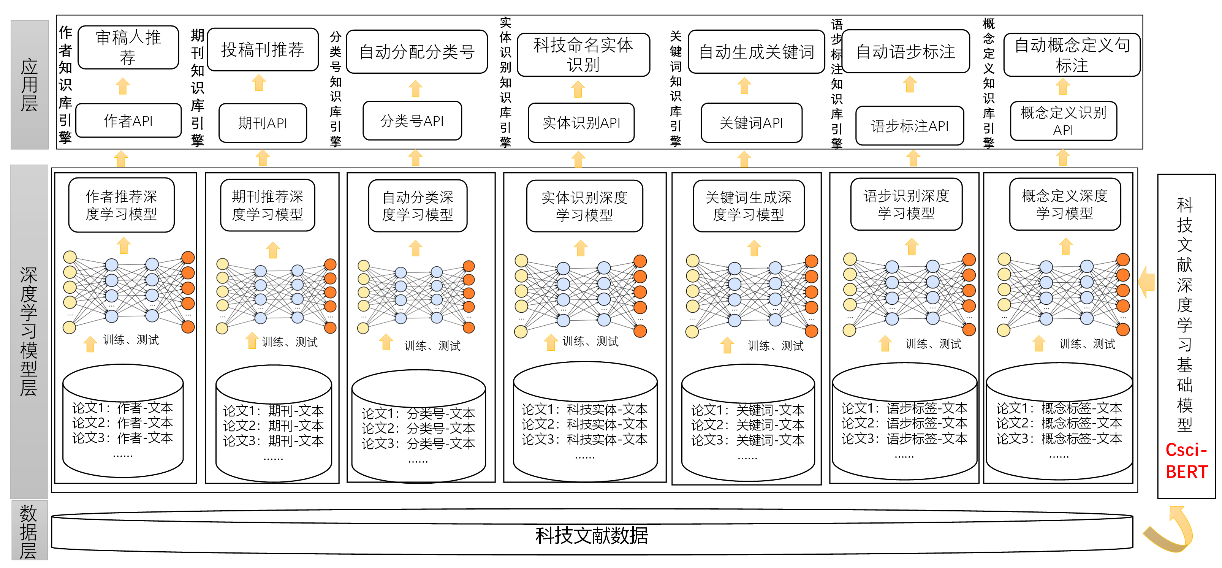
- Build a knowledge engine for scientific and technological literature based on deep learning
Main Research Content
CsciBERT will use a large amount of scientific and technological literature text content to construct a language model in a self-supervised learning manner, establishing a pre-training language model for Chinese scientific papers. CsciBERT will serve as a general pre-training language model for Chinese scientific literature across all fields, building specific language models for specific knowledge mining and analysis needs in different academic fields.
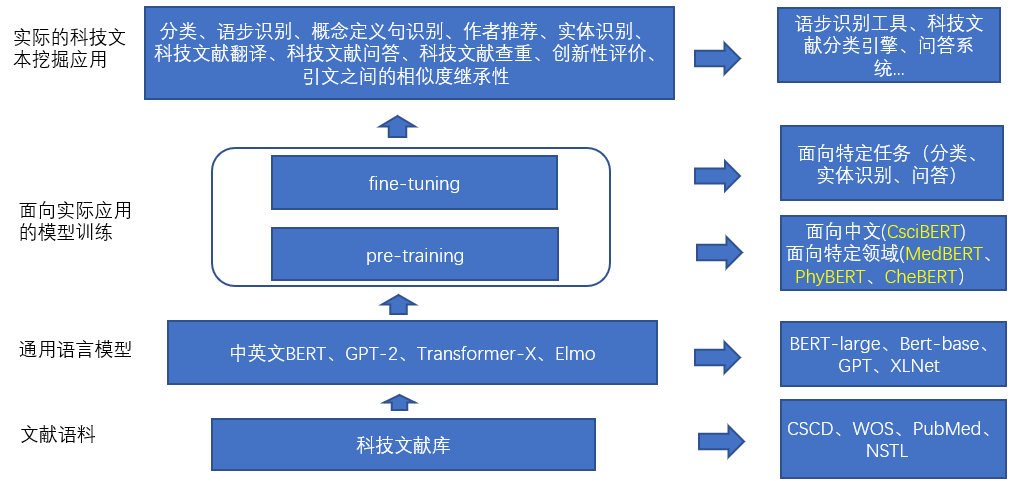
Upon completing the construction of the Chinese scientific paper pre-training model CsciBERT, the project will further address the actual needs of literature and information work, fully exploit scientific and technological literature resources, and transform the literature database into an engine of scientific knowledge.
Project Four:National Science and Technology Library (NSTL): "Overall Design and Key Technology R&D Special Project for the Next Generation Open Knowledge Service Platform - Development of a Deep Learning-Based Scientific Paper Rhetorical Move Annotation Tool"
Project Background
Rhetorical move, also known as rhetorical move (Rhetorical Move), is a concept in stylistics, first proposed by Swales, which refers to a rhetorical unit that performs a coherent communicative function. Most current journal papers still use unstructured abstracts, and the rhetorical move content of each abstract is mixed in the entire abstract paragraph, making it difficult for readers to quickly read and grasp the related rhetorical move content of these unstructured abstracts. Automatic recognition of rhetorical moves in unstructured abstracts of scientific papers can effectively find sentences expressing research purposes, methods, results, and conclusions in scientific papers, allowing readers to quickly grasp the main content of scientific papers, and has significant implications for revealing scientific knowledge in scientific papers.
Overall Goal
This project undertakes the text big data analysis sub-task in the next-generation open knowledge service platform, and by realizing the automatic annotation of rhetorical moves, it reveals the knowledge content in a large amount of scientific literature at the sentence level, and provides a rhetorical move annotation function interface for the next-generation open knowledge service platform, thereby helping to realize the semantic intelligent retrieval application of the platform, and is conducive to providing knowledge services at a deeper level.
Main Research Content
To realize the automatic recognition of rhetorical moves in scientific papers, we first constructed a dataset through the acquisition of a large amount of structured abstract text. Then, we compared and analyzed the applications of various deep learning methods in automatic rhetorical move recognition, and for the current best-performing BERT model, we completed model optimization and improvement based on the pre-training + fine-tuning model, and achieved significant performance improvement in rhetorical move recognition. Regarding the issue of dataset quality, we refined and optimized the corpus library, further improving the practical test results of rhetorical move recognition. For practical application scenarios, we improved the call efficiency of deep learning models through model compression and microservice construction, forming an efficient and usable rhetorical move recognition tool.
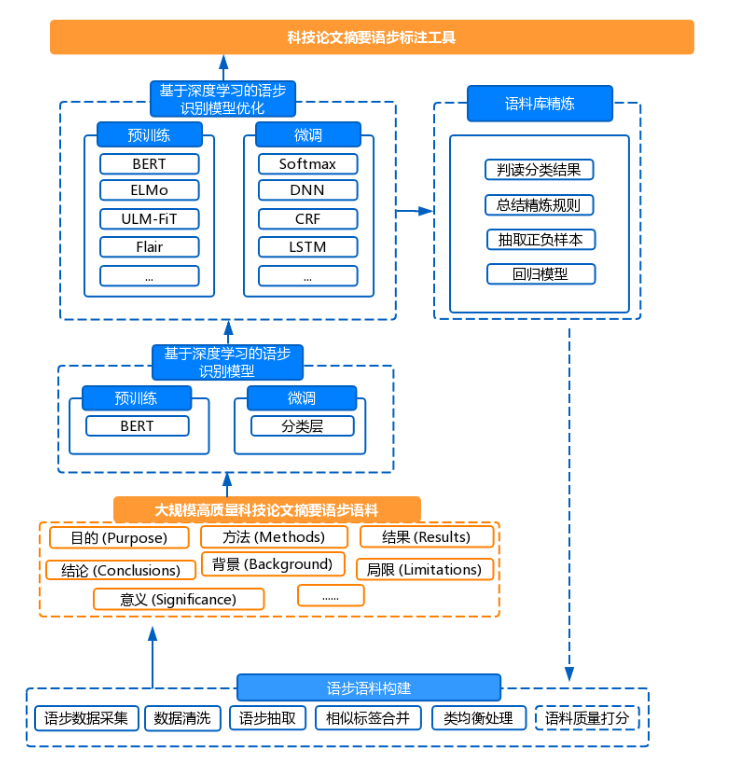
Project Five:Information Center of the Chinese Academy of Sciences: "Demonstration of Rich Semantic Retrieval Application of Scientific and Technological Literature"
Demonstration Platform:Automatic Semantic Annotation Retrieval System for Scientific Research Papers in the Field of Physics
Project Background
Rich Semantics, in contrast to Semantics in a general sense, is a composite of multiple types of semantic elements organically combined together, with structured, modeled characteristics. The emergence of this new concept of Rich Semantics has received high attention in the digital library field. This project will establish a demonstration application system for rich semantic retrieval of scientific and technological literature in the field of high-energy physics. This system will help to reveal the implicit knowledge in scientific and technological literature, make the rich semantics of scientific and technological literature more convenient for users to discover and use, promote the improvement of the technical capabilities of digital libraries in knowledge extraction, text mining, precise searching, knowledge organization, etc., and the project results will have significant academic value and application value, producing a considerable scale of application demonstration effect.
Overall Goal
This project selects the field of high-energy physics, integrates and optimizes existing key technologies for semantic annotation, semantic organization, and semantic indexing, and makes full use of existing semantic resources to build a demonstration application system for rich semantic retrieval of scientific and technological literature.
Main Research Content
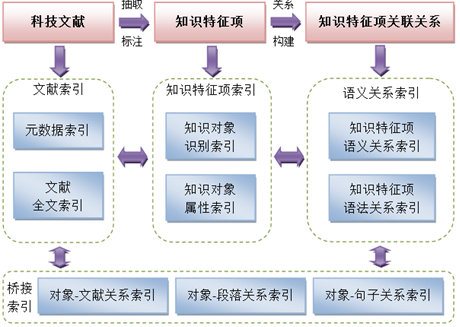
This project proposes a multi-level semantic annotation model for scientific and technological papers, and develops tools to automatically annotate and reveal semantic elements and related relationships at each level. From the four levels of paragraph, discourse, sentence, and concept, automatic annotations are applied to knowledge feature items with significant semantic connotations in scientific articles.
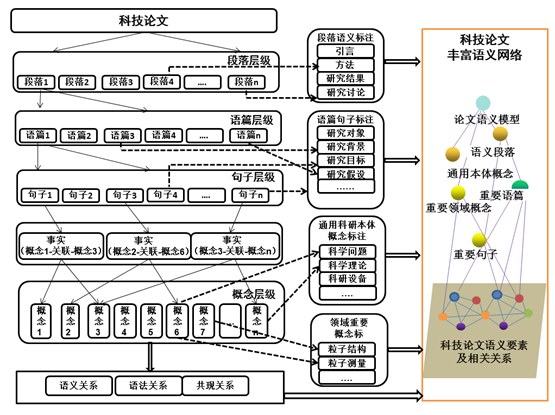
This project develops the construction of indexes for scientific and technological literature knowledge objects from four dimensions: literature, knowledge feature items, potential semantic/grammatical relationships between knowledge feature items, and bridging mappings. This allows for the realization of facet indexing at the semantic level and relation inference retrieval in the rich semantic network of knowledge nodes.